Betterment's tax-loss harvesting methodology
Tax loss harvesting is a sophisticated technique to get more value from your investments—but doing it well requires expertise.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Navigating the “Wash Sale” rule
- The Betterment solution
- Tax loss harvesting model calibration
- Best practices for TLH
- How we calculate the value of tax loss harvesting
- Your personalized Estimated Tax Savings tool
- Conclusion
There are many ways to get your investments to work harder for you— diversification, downside risk management, and an appropriate mix of asset classes tailored to your recommended allocation. Betterment does this automatically via its ETF portfolios.
But there is another way to help you get more out of your portfolio—using investment losses to improve your after-tax returns with a method called tax loss harvesting. In this article, we introduce Betterment’s tax loss harvesting (TLH): a sophisticated, fully automated tool that Betterment customers can choose to enable.
Betterment’s tax loss harvesting service scans portfolios regularly for opportunities (temporary dips that result from market volatility) for opportunities to realize losses which can be valuable come tax time. While the concept of tax loss harvesting is not new for wealthy investors, tax loss harvesting utilizes a number of innovations that typical implementations may lack. It takes a holistic approach to tax-efficiency, seeking to optimize user-initiated transactions in addition to adding value through automated activity, such as rebalances.
What is tax loss harvesting?
Capital losses can lower your tax bill by offsetting gains, but the only way to realize a loss is to sell the depreciated asset. However, in a well-allocated portfolio, each asset plays an essential role in providing a piece of total market exposure. For that reason, an investor should not want to give up potential expected returns associated with each asset just to realize a loss.
At its most basic level, tax loss harvesting is selling a security that has experienced a loss—and then buying a correlated asset (i.e. one that provides similar exposure) to replace it. The strategy has two benefits: it allows the investor to “harvest” a valuable loss, and it keeps the portfolio balanced at the desired allocation.
How can it lower your tax bill?
Capital losses can be used to offset capital gains you’ve realized in other transactions over the course of a year—gains on which you would otherwise owe tax. Then, if there are losses left over (or if there were no gains to offset), you can offset up to $3,000 of ordinary income for the year. If any losses still remain, they can be carried forward indefinitely.
Tax loss harvesting is primarily a tax deferral strategy, and its benefit depends entirely on individual circumstances. Over the long run, it can add value through some combination of these distinct benefits that it seeks to provide:
- Tax deferral: Losses harvested can be used to offset unavoidable gains in the portfolio, or capital gains elsewhere (e.g., from selling real estate), deferring the tax owed. Savings that are invested may grow, assuming a conservative growth rate of 5% over a 10-year period, a dollar of tax deferred would be worth $1.63. Even after belatedly parting with the dollar, and paying tax on the $0.63 of growth, you’re ahead.
- Pushing capital gains into a lower tax rate: If you’ve realized short-term capital gains (STCG) this year, they’ll generally be taxed at your highest rate. However, if you’ve harvested losses to offset them, the corresponding gain you owe in the future could be long-term capital gain (LTCG). You’ve effectively turned a gain that would have been taxed up to 50% today into a gain that will be taxed more lightly in the future (up to 30%).
- Converting ordinary income into long-term capital gains: A variation on the above: offsetting up to $3,000 from your ordinary income shields that amount from your top marginal rate, but the offsetting future gain will likely be taxed at the LTCG rate.
- Permanent tax avoidance in certain circumstances: tax loss harvesting provides benefits now in exchange for increasing built-in gains, subject to tax later. However, under certain circumstances (charitable donation, bequest to heirs), these gains may avoid taxation entirely.
Navigating the "Wash Sale" rule
Summary: Wash sale rule management is at the core of any tax loss harvesting strategy. Unsophisticated approaches can detract from the value of the harvest or place constraints on customer cash flows in order to function.
At a high level, the so-called "Wash Sale” rule disallows a loss from selling a security if a “substantially identical” security is purchased 30 days after or before the sale. The rationale is that a taxpayer should not enjoy the benefit of deducting a loss if they did not truly dispose of the security.
The wash sale rule applies not just to situations when a “substantially identical” purchase is made in the same account, but also when the purchase is made in the individual’s IRA/401(k) account, or even in a spouse’s account. This broad application of the wash sale rule seeks to ensure that investors cannot utilize nominally different accounts to maintain their ownership, and still benefit from the loss.
A wash sale involving an IRA/401(k) account is particularly unfavorable. Generally, a “washed” loss is postponed until the replacement is sold, but if the replacement is purchased in an IRA/401(k) account, the loss is permanently disallowed.
If not managed correctly, wash sales can undermine tax loss harvesting. Handling proceeds from the harvest is not the sole concern—any deposits made in the following 30 days (whether into the same account, or into the individual’s IRA/401(k)) also need to be allocated with care.
Minimizing the wash
The simplest way to avoid triggering a wash sale is to avoid purchasing any security at all for the 30 days following the harvest, keeping the proceeds (and any inflows during that period) in cash. This approach, however, would systematically keep a portion of the portfolio out of the market. Over the long term, this “cash drag” could hurt the portfolio’s performance.
More advanced strategies repurchase an asset with similar exposure to the harvested security that is not “substantially identical” for purposes of the wash sale rule. In the case of an individual stock, it is clear that repurchasing stock of that same company would violate the rule. Less clear is the treatment of two index funds from different issuers (e.g., Vanguard and Schwab) that track the same index. While the IRS has not issued any guidance to suggest that such two funds are “substantially identical,” a more conservative approach when dealing with an index fund portfolio would be to repurchase a fund whose performance correlates closely with that of the harvested fund, but tracks a different index.
Tax loss harvesting is generally designed around this index-based logic and generally seeks to reduce wash sales, although it cannot avoid potential wash sales arising from transactions in tickers that track the same index where one of the tickers is not currently a primary, secondary, or tertiary ticker (as those terms are defined in this white paper). This situation could arise, for example, when other tickers are transferred to Betterment or where they were previously a primary, secondary, or tertiary ticker. Additionally, for some portfolios constructed by third parties (e.g., Vanguard, Blackrock, or Goldman Sachs), certain secondary and tertiary tickers track the same index. Certain asset classes in portfolios constructed by third parties (e.g., Vanguard, Blackrock, or Goldman Sachs) do not have tertiary tickers, such that permanently disallowed losses could occur if there were overlapping holdings in taxable and tax-advantaged accounts. Betterment’s TLH feature may also permit wash sales where the anticipated tax benefit of the overall harvest transaction sufficiently outweighs the impact of expected washed losses .
Selecting a viable replacement security is just one piece of the accounting and optimization puzzle. Manually implementing a tax loss harvesting strategy is feasible with a handful of securities, little to no cash flows, and infrequent harvests. Assets may however dip in value but potentially recover by the end of the year, therefore annual strategies or infrequent harvests may leave many losses on the table. The wash sale management and tax lot accounting necessary to support more frequent harvesting quickly becomes overwhelming in a multi-asset portfolio—especially with regular deposits, dividends, and rebalancing.
An effective loss harvesting algorithm should be able to maximize harvesting opportunities across a full range of volatility scenarios, without sacrificing the investor’s global asset allocation. It should reinvest harvest proceeds into correlated alternate assets, all while handling unforeseen cash inflows from the investor without ever resorting to cash positions. It should also be able to monitor each tax lot individually, harvesting individual lots at an opportune time, which may depend on the volatility of the asset. Tax loss harvesting was created because no available implementations seemed to solve all of these problems.
Existing strategies and their limitations
Every tax loss harvesting strategy shares the same basic goal: to maximize a portfolio’s after-tax returns by realizing built-in losses while minimizing the negative impact of wash sales.
Approaches to tax loss harvesting differ primarily in how they handle the proceeds of the harvest to avoid a wash sale. Below are the three strategies commonly employed by manual and algorithmic implementations.
After selling a security that has experienced a loss, existing strategies would likely have you:
|
Existing strategy |
Problem |
|
Delay reinvesting the proceeds of a harvest for 30 days, thereby ensuring that the repurchase will not trigger a wash sale. |
While it’s the easiest method to implement, it has a major drawback: no market exposure—also called cash drag. Cash drag hurts portfolio returns over the long term, and could offset any potential benefit from tax loss harvesting. |
|
Reallocate the cash into one or more entirely different asset classes in the portfolio. |
This method throws off an investor’s desired asset allocation. Additionally, such purchases may block other harvests over the next 30 days by setting up potential wash sales in those other asset classes. |
|
Switch back to original security after 30 days from the replacement security. Common manual approach, also used by some automated investing services. |
A switchback can trigger short-term capital gains when selling the replacement security, reducing the tax benefit of the harvest. Even worse, this strategy can leave an investor owing more tax than if it did nothing. |
The hazards of switchbacks
In the 30 days leading up to the switchback, two things can happen: the replacement security can drop further, or go up. If it goes down, the switchback will realize an additional loss. However, if it goes up, which is what any asset with a positive expected return is expected to do over any given period, the switchback will realize short-term capital gains (STCG)—kryptonite to a tax-efficient portfolio management strategy.
An attempt to mitigate this risk could be setting a higher threshold based on volatility of the asset class—only harvesting when the loss is so deep that the asset is unlikely to entirely recover in 30 days. Of course, there is still no guarantee that it will not, and the price paid for this buffer is that your lower-yielding harvests will also be less frequent than they could be with a more sophisticated strategy.
Examples of negative tax arbitrage
Negative tax arbitrage with automatic 30-day switchback
An automatic 30-day switchback can destroy the value of the harvested loss, and even increase tax owed, rather than reduce it. A substantial dip presents an excellent opportunity to sell an entire position and harvest a long-term loss. Proceeds will then be re-invested in a highly correlated replacement (tracking a different index). 30 days after the sale, the dip proved temporary and the asset class more than recovered. The switchback sale results in STCG in excess of the loss that was harvested, and actually leaves the investor owing tax, whereas without the harvest, they would have owed nothing.
Due to a technical nuance in the way gains and losses are netted, the 30- day switchback can result in negative tax arbitrage, by effectively pushing existing gains into a higher tax rate.
When adding up gains and losses for the year, the rules require netting of like against like first. If any long-term capital gain (LTCG) is present for the year, you must net a long-term capital loss (LTCL) against that first, and only then against any STCG.
Negative tax arbitrage when unrelated long-term gains are present
Now let’s assume the taxpayer realized a LTCG. If no harvest takes place, the investor will owe tax on the gain at the lower LTCG rate. However, if you add the LTCL harvest and STCG switchback trades, the rules now require that the harvested LTCL is applied first against the unrelated LTCG. The harvested LTCL gets used up entirely, exposing the entire STCG from the switchback as taxable. Instead of sheltering the highly taxed gain on the switchback, the harvested loss got used up sheltering a lower-taxed gain, creating far greater tax liability than if no harvest had taken place.
In the presence of unrelated transactions, unsophisticated harvesting can effectively convert existing LTCG into STCG. Some investors regularly generate significant LTCG (for instance, by gradually diversifying out of a highly appreciated position in a single stock). It’s these investors, in fact, who would benefit the most from effective tax loss harvesting.
Negative tax arbitrage with dividends
Negative tax arbitrage can result in connection with dividend payments. If certain conditions are met, some ETF distributions are treated as “qualified dividends”, taxed at lower rates. One condition is holding the security for more than 60 days. If the dividend is paid while the position is in the replacement security, it will not get this favorable treatment: under a rigid 30-day switchback, the condition can never be met. As a result, up to 20% of the dividend is lost to tax (the difference between the higher and lower rate).
The Betterment solution
Summary: Betterment’s tax loss harvesting approaches tax-efficiency holistically, seeking to optimize transactions, including customer activity.
The benefits tax loss harvesting seeks to deliver, include:
- No exposure to short-term capital gains in an attempt to harvest losses. Through our proprietary Parallel Position Management (PPM) system, a dual-security asset class approach enforces preference for one security without needlessly triggering capital gains in an attempt to harvest losses, all without putting constraints on customer cash flows.
- No negative tax arbitrage traps associated with less sophisticated harvesting strategies (e.g., 30-day switchback), making tax loss harvesting especially suited for those generating large long-term capital gains on an ongoing basis.
- Zero cash drag. With fractional shares and seamless handling of all inflows during wash sale windows, every dollar of your ETF portfolio is invested.
- Tax loss preservation logic extended to user-realized losses, not just harvested losses, automatically protecting both from the wash sale rule. In short, user withdrawals always sell any losses first.
- No disallowed losses through overlap with a Betterment IRA/401(k). We use a tertiary ticker system to eliminate the possibility of permanently disallowed losses triggered by subsequent IRA/401(k) activity.² This makes TLH ideal for those who invest in both taxable and tax-advantaged accounts.
- Harvests also take the opportunity to rebalance across all asset classes, rather than re-invest solely within the same asset class. This further reduces the need to rebalance during volatile stretches, which means fewer realized gains, and higher tax alpha.
Through these innovations, tax loss harvesting creates significant value over manually-serviced or less sophisticated algorithmic implementations. Tax loss harvesting is accessible to investors —fully automated, effective, and at no additional cost.
Parallel securities
To ensure that each asset class is supported by optimal securities in both primary and alternate (secondary) positions, we screened by expense ratio, liquidity (bid-ask spread), tracking error vs. benchmark, and most importantly, covariance of the alternate with the primary.1
While there are small cost differences between the primary and alternate securities, the cost of negative tax arbitrage from tax-agnostic switching vastly outweighs the cost of maintaining a dual position within an asset class.
Tax loss harvesting features a special mechanism for coordination with IRAs/401(k)s that requires us to pick a third (tertiary) security in each harvestable asset class (except in municipal bonds, which are not in the IRA/401(k) portfolio). While these have a higher cost than the primary and alternate, they are not expected to be utilized often, and even then, for short durations (more below in IRA/401(k) protection).
Parallel position management
As demonstrated, the unconditional 30-day switchback to the primary security is problematic for a number of reasons. To fix those problems, we engineered a platform to support tax loss harvesting, which seeks to tax-optimize user and system-initiated transactions: the Parallel Position Management (PPM) system.
PPM allows each asset class to contain a primary security to represent the desired exposure while maintaining alternate and tertiary securities that are closely correlated securities, should that result in a better after-tax outcome.
PPM provides several improvements over the switchback strategy. First, unnecessary gains are minimized. Second, the parallel security (could be primary or alternate) serves as a safe harbor to reduce potential wash sales—not just from harvest proceeds, but any cash inflows. Third, the mechanism seeks to protect not just harvested losses, but losses realized by the customer as well.
PPM not only facilitates effective opportunities for tax loss harvesting, but also extends maximum tax-efficiency to customer-initiated transactions. Every customer withdrawal is a potential harvest (losses are sold first). And every customer deposit and dividend is routed to the parallel position that would reduce wash sales, while shoring up the target allocation.
PPM has a preference for the primary security when rebalancing and for all cash flow events—but always subject to tax considerations. This is how PPM behaves under various conditions:
|
Transaction |
PPM behavior |
|
Withdrawals and sales from rebalancing |
Sales default out of the alternate position (if such a position exists), but not at the expense of triggering STCG—in that case, PPM will sell lots of the primary security first. Rebalancing will attempt to stop short of realizing STCG. Taxable gains are minimized at every decision point—STCG tax lots are the last to be sold on a user withdrawal. |
|
Deposits, buys from rebalancing, and dividend reinvestments |
PPM directs inflows to underweight asset classes, and within each asset class, into the primary, unless doing so incurs greater wash sale costs than buying the alternate. |
|
Harvest events |
TLH harvests can come out of the primary into the alternate, or vice versa, depending on which harvest has a greater expected value. After an initial harvest, it could make sense at some point to harvest back into the primary, to harvest more of the remaining primary into the alternate, or to do nothing. |
Wash sale management
Managing cash flows across both taxable and IRA/401(k) accounts without washing realized losses is a complex problem.
Tax loss harvesting operates without constraining the way that customers prefer contributing to their portfolios, and without resorting to cash positions. With the benefit of parallel positions, Betterment weighs wash sale implications of deposits,withdrawals and dividend reinvestment This system protects not just harvested losses, but also losses realized through withdrawals.
Minimizing wash sale through tertiary tickers in IRA/401(k)
Because IRA/401(k) wash sales are particularly unfavorable—the loss is disallowed permanently—tax loss harvesting ensures that no loss realized in the taxable account is washed by a subsequent deposit into a Betterment IRA/401(k) with a tertiary ticker system in IRA/401(K) and no harvesting is done in IRA/401(k).
Let’s look at an example of how tax loss harvesting handles a potentially disruptive IRA inflow with a tertiary ticker when there are realized losses to protect, using real market data for a Developed Markets asset class.
The customer starts with a position in VEA, the primary security, in both the taxable and IRA accounts. We harvest a loss by selling the entire taxable position, and then repurchasing the alternate security, SCHF.
Loss harvested in VEA
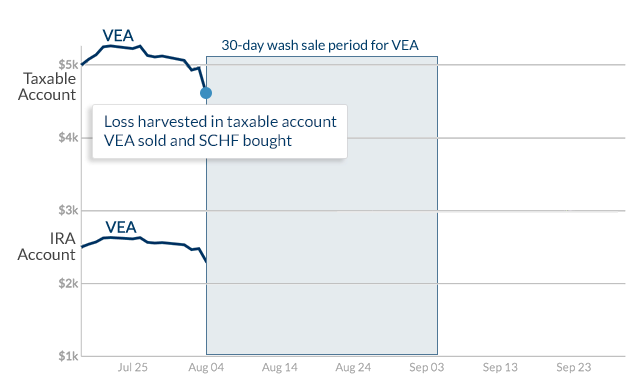
Two weeks pass, and the customer makes a withdrawal from the taxable account (the entire SCHF position, for simplicity), intending to fund the IRA. In those two weeks, the asset class dropped more, so the sale of SCHF also realized a loss. The VEA position in the IRA remains unchanged.
Customer withdrawal sells SCHF at a loss
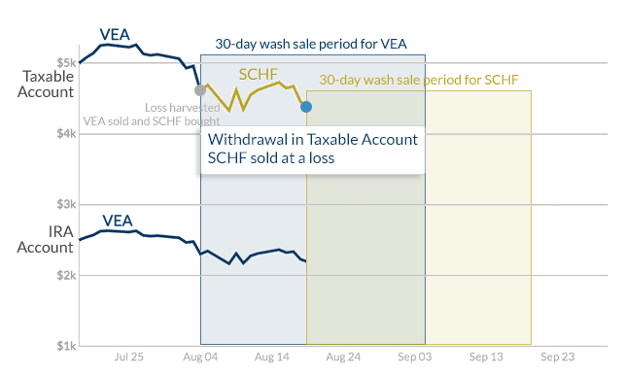
A few days later, the customer contributes to his IRA, and $1,000 is allocated to the Developed Markets asset class, which already contains some VEA. Despite the fact that the customer no longer holds any VEA or SCHF in his taxable account, buying either one in the IRA would permanently wash a valuable realized loss. The Tertiary Ticker System automatically allocates the inflow into the third option for developed markets, IEFA.
IRA deposit into tertiary Ticker
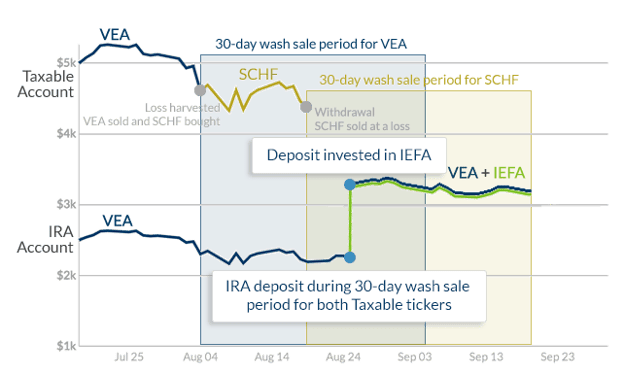
Both losses have been preserved, and the customer now holds VEA and IEFA in his IRA, maintaining desired allocation at all times. Because no capital gains are realized in an IRA/401(k), there is no harm in switching out of the IEFA position and consolidating the entire asset class in VEA when there is no danger of a wash sale.
The result: Customers using TLH who also have their IRA/401(k) assets with Betterment can know that Betterment will seek to protect valuable realized losses whenever they deposit into their IRA/401(k), whether it’s lump rollover, auto-deposits or even dividend reinvestments.
Smart rebalancing
Lastly, tax loss harvesting directs the proceeds of every harvest to rebalance the entire portfolio, the same way that a Betterment account handles any incoming cash flow (deposit, dividend). Most of the cash is expected to stay in that asset class and be reinvested into the parallel asset, but some of it may not. Recognizing every harvest as a rebalancing opportunity further reduces the need for additional selling in times of volatility, further reducing tax liability. As always, fractional shares allow the inflows to be allocated with precision.
Tax loss harvesting model calibration
Summary: To make harvesting decisions, tax loss harvesting optimizes around multiple inputs, derived from rigorous Monte Carlo simulations.
The decision to harvest is made when the benefit, net of cost, exceeds a certain threshold. The potential benefit of a harvest is discussed in detail below (“Results”). Unlike a 30-day switchback strategy, tax loss harvesting does not incur the expected STCG cost of the switchback trade. Therefore, “cost” consists of three components: trading expense, execution expense, and increased cost of ownership for the replacement asset (if any).
Trading costs are included in the wrap fee paid by Betterment customers. Tax loss harvesting is engineered to factor in the other two components, configurable at the asset level, and the resulting cost approaches negligible. Bid-ask spreads for the bulk of harvestable assets are narrow. We seek funds with expense ratios for the major primary/alternate ETF pairs that are close, and in the case where a harvest back to the primary ticker is being evaluated, that difference is actually a benefit, not a cost.
There are two general approaches to testing a model’s performance: historical backtesting and forward-looking simulation. Optimizing a system to deliver the best results for only past historical periods is relatively trivial, but doing so would be a classic instance of data snooping bias. Relying solely on a historical backtest of a portfolio composed of ETFs that allow for 10 to 20 years of reliable data when designing a system intended to provide 40 to 50 years of benefit would mean making a number of indefensible assumptions about general market behavior.
The superset of decision variables driving tax loss harvesting is beyond the scope of this paper—optimizing around these variables required exhaustive analysis. Tax loss harvesting was calibrated via Betterment’s rigorous Monte Carlo simulation framework, spinning up thousands of server instances in the cloud to run through tens of thousands of forward-looking scenarios testing model performance. We have calibrated tax loss harvesting in a way that we believe optimizes its effectiveness given expected future returns and volatility, but other optimizations could result in more frequent harvests or better results depending on actual market conditions.
Best practices for tax loss harvesting
Summary: Tax loss harvesting can add some value for most investors, but high earners with a combination of long time horizons, ongoing realized gains, and plans for some charitable disposition will reap the largest benefits.
This is a good point to reiterate that tax loss harvesting delivers value primarily due to tax deferral, not tax avoidance. A harvested loss can be beneficial in the current tax year to varying degrees, but harvesting that loss generally means creating an offsetting gain at some point in the future. If and when the portfolio is liquidated, the gain realized will be higher than if the harvest never took place.
Let’s look at an example:
Year 1: Buy asset A for $100.
Year 2: Asset A drops to $90. Harvest $10 loss, repurchase similar Asset B for $90.
Year 20: Asset B is worth $500 and is liquidated. Gains of $410 realized (sale price minus cost basis of $90)
Had the harvest never happened, we’d be selling A with a basis of $100, and gains realized would only be $400 (assuming similar performance from the two correlated assets.) Harvesting the $10 loss allows us to offset some unrelated $10 gain today, but at a price of an offsetting $10 gain at some point in the future.
The value of a harvest largely depends on two things. First, what income, if any, is available for offset? Second, how much time will elapse before the portfolio is liquidated? As the deferral period grows, so does the benefit—the reinvested savings from the tax deferral have more time to grow.
While nothing herein should be interpreted as tax advice, examining some sample investor profiles is a good way to appreciate the nature of the benefit of tax loss harvesting.
Who benefits most?
The Bottomless Gains Investor: A capital loss is only as valuable as the tax saved on the gain it offsets. Some investors may incur substantial capital gains every year from selling highly appreciated assets—other securities, or perhaps real estate. These investors can immediately use all the harvested losses, offsetting gains and generating substantial tax savings.
The High Income Earner: Harvesting can have real benefits even in the absence of gains. Each year, up to $3,000 of capital losses can be deducted from ordinary income. Earners in high income tax states (such as New York or California) could be subject to a combined marginal tax bracket of up to 50%. Taking the full deduction, these investors could save $1,500 on their tax bill that year.
What’s more, this deduction could benefit from positive rate arbitrage. The offsetting gain is likely to be LTCG, taxed at around 30% for the high earner—less than $1,000—a real tax savings of over $500, on top of any deferral value.
The Steady Saver: An initial investment may present some harvesting opportunities in the first few years, but over the long term, it’s increasingly unlikely that the value of an asset drops below the initial purchase price, even in down years. Regular deposits create multiple price points, which may create more harvesting opportunities over time. (This is not a rationale for keeping money out of the market and dripping it in over time—tax loss harvesting is an optimization around returns, not a substitute for market exposure.)
The Philanthropist: In each scenario above, any benefit is amplified by the length of the deferral period before the offsetting gains are eventually realized. However, if the appreciated securities are donated to charity or passed down to heirs, the tax can be avoided entirely. When coupled with this outcome, the scenarios above deliver the maximum benefit of TLH. Wealthy investors have long used the dual strategy of loss harvesting and charitable giving.
Even if an investor expects to mostly liquidate, any gifting will unlock some of this benefit. Using losses today, in exchange for built-in gains, offers the partial philanthropist a number of tax-efficient options later in life.
Who benefits least?
The Aspiring Tax Bracket Climber: Tax deferral is undesirable if your future tax bracket will be higher than your current. If you expect to achieve (or return to) substantially higher income in the future, tax loss harvesting may be exactly the wrong strategy—it may, in fact, make sense to harvest gains, not losses.
In particular, we do not advise you to use tax loss harvesting if you can currently realize capital gains at a 0% tax rate. Under 2025 tax brackets, this may be the case if your taxable income is below $48,350 as a single filer or $96,700 if you are married filing jointly. See the IRS website for more details.
Graduate students, those taking parental leave, or just starting out in their careers should ask “What tax rate am I offsetting today” versus “What rate can I reasonably expect to pay in the future?”
The Scattered Portfolio: Tax loss harvesting is carefully calibrated to manage wash sales across all assets managed by Betterment, including IRA assets. However, the algorithms cannot take into account information that is not available. To the extent that a Betterment customer’s holdings (or a spouse’s holdings) in another account overlap with the Betterment portfolio, there can be no guarantee that tax loss harvesting activity will not conflict with sales and purchases in those other accounts (including dividend reinvestments), and result in unforeseen wash sales that reverse some or all of the benefits of tax loss harvesting. We do not recommend tax loss harvesting to a customer who holds (or whose spouse holds) any of the ETFs in the Betterment portfolio in non-Betterment accounts. You can ask Betterment to coordinate tax loss harvesting with your spouse’s account at Betterment. You’ll be asked for your spouse’s account information after you enable tax loss harvesting so that we can help optimize your investments across your accounts.
The Portfolio Strategy Collector: Electing different portfolio strategies for multiple Betterment goals may cause tax loss harvesting to identify fewer opportunities to harvest losses than it might if you elect the same portfolio strategy for all of your Betterment goals.
The Rapid Liquidator: What happens if all of the additional gains due to harvesting are realized over the course of a single year? In a full liquidation of a long-standing portfolio, the additional gains due to harvesting could push the taxpayer into a higher LTCG bracket, potentially reversing the benefit of tax loss harvesting. For those who expect to draw down with more flexibility, smart automation will be there to help optimize the tax consequences.
The Imminent Withdrawal: The harvesting of tax losses resets the one-year holding period that is used to distinguish between LTCG and STCG. For most investors, this isn’t an issue: by the time that they sell the impacted investments, the one-year holding period has elapsed and they pay taxes at the lower LTCG rate. This is particularly true for Betterment customers because our TaxMin feature automatically realizes LTCG ahead of STCG in response to a withdrawal request. However, if you are planning to withdraw a large portion of your taxable assets in the next 12 months, you should wait to turn on tax loss harvesting until after the withdrawal is complete to reduce the possibility of realizing STCG.
Other impacts to consider
Investors with assets held in different portfolio strategies should understand how it impacts the operation of tax loss harvesting. To learn more, please see Betterment’s SRI disclosures, Flexible portfolio disclosures, the Goldman Sachs smart beta disclosures, and the BlackRock target income portfolio disclosures for further detail. Clients in Advisor-designed custom portfolios through Betterment for Advisors should consult their Advisors to understand the limitations of tax loss harvesting with respect to any custom portfolio. Additionally, as described above, electing one portfolio strategy for one or more goals in your account while simultaneously electing a different portfolio for other goals in your account may reduce opportunities for TLH to harvest losses, as TLH is calibrated to seek to reduce wash sales.
Due to Betterment’s monthly cadence for billing fees for advisory services, through the liquidation of securities, tax loss harvesting opportunities may be adversely affected for customers with particularly high stock allocations, third party portfolios, or flexible portfolios. As a result of assessing fees on a monthly cadence for a customer with only equity security exposure, which tends to be more opportunistic for tax loss harvesting, certain securities may be sold that could have been used to tax loss harvest at a later date, thereby delaying the harvesting opportunity into the future. This delay would be due to the TLH tool’s effort to reduce instances of triggering the wash sale rule, which forbids a security from being sold only to be replaced with a “substantially similar” security within a 30-day period.
Factors which will determine the actual benefit of tax loss harvesting include, but are not limited to, market performance, the size of the portfolio, the stock exposure of the portfolio, the frequency and size of deposits into the portfolio, the availability of capital gains and income which can be offset by losses harvested, the tax rates applicable to the investor in a given tax year and in future years, the extent to which relevant assets in the portfolio are donated to charity or bequeathed to heirs, and the time elapsed before liquidation of any assets that are not disposed of in this manner.
All of Betterment’s trading decisions are discretionary and Betterment may decide to limit or postpone TLH trading on any given day or on consecutive days, either with respect to a single account or across multiple accounts.
Tax loss harvesting is not suitable for all investors. Nothing herein should be interpreted as tax advice, and Betterment does not represent in any manner that the tax consequences described herein will be obtained, or that any Betterment product will result in any particular tax consequence. Please consult your personal tax advisor as to whether TLH is a suitable strategy for you, given your particular circumstances. The tax consequences of tax loss harvesting are complex and uncertain and may be challenged by the IRS. You and your tax advisor are responsible for how transactions conducted in your account are reported to the IRS on your personal tax return. Betterment assumes no responsibility for the tax consequences to any client of any transaction.
See Betterment’s tax loss harvesting disclosures for further detail.
How we calculate the value of tax loss harvesting
Over 2022 and 2023, we calculated that 69% of Betterment customers who employed the strategy saw potential savings in excess of the Betterment fees charged on their taxable accounts for the year.
To reach this conclusion, we first identified the accounts to consider, defined as taxable investing accounts that had a positive balance and tax loss harvesting turned on throughout 2022 and 2023. We excluded trust accounts because their tax treatments can be highly-specific and they made up less than 1% of the data.
For each account’s taxpayer, we pulled the short and long term capital gain/loss in the relevant accounts realized in 2022 and 2023 using our trading and tax records. We then divided the gain/loss into those caused by a TLH transaction and those not caused by a TLH transaction.
Then, for each tax year, we calculated the short-term gains offset by taking the greater of the short-term loss realized by tax loss harvesting and the short-term gain caused by other transactions. We did the same for long-term gain/loss. If there were any losses leftover, we calculated the amount of ordinary income that could be offset by taking the greater of the customer’s reported income and $3,000 ($1,500 if the customer is married filing separately) and then taking the greater of that number and the sum of the remaining long-term and short-term losses (after first subtracting any non-tax loss harvesting losses from ordinary income). If there were any losses leftover in 2022 after all that, we carried those losses forward to 2023.
At this point, we had for each customer the amount of short-term gains, long-term gains and ordinary income offset by tax loss harvesting for each tax year. We then calculated the short-term and long-term capital gains rates using the federal tax brackets for 2022 and 2023 and the reported income of the taxpayer, their reported tax filing status, and their reported number of dependents. We assumed the standard deduction and conservatively did not include state capital gains taxes because some states do not have capital gains tax. We calculated the ordinary income rate including federal taxes, state taxes, and Medicare and Social Security taxes using the user’s reported income, filing status, number of dependents, assumed standard deduction, and age (assuming Medicare and Social Security taxes cease at the retirement age of 67). We then applied these tax rates respectively to the offsets to get the tax bill reduction from each type of offset and summed them up to get the total tax reduction.
Then, we pulled the total fees charged to the users on the account in question that were accrued in 2022 and 2023 from our fee accrual records and compared that to the tax bill reduction. If the tax bill reduction was greater than the fees, we considered tax loss harvesting to have indirectly paid for the fees in the account in question for the taxpayer in question. This was the case for 69% of customers.
Your personalized Estimated Tax Savings tool
Overview: Betterment’s TLH Estimated Tax Savings Tool is found in your online account and designed to quantify the tax-saving potential of our tax loss harvesting (TLH) feature. By leveraging both transactional data from Betterment accounts and your self-reported demographic and financial profile information, the tool generates dynamic estimates of realized and potential tax savings. These calculations provide both current-year and cumulative ("all-time") tax savings estimates.
Client-centric tax modeling: To personalize estimates, the tool takes into account client financial profile information: your self-reported annual pre-tax income, state of residence, tax filing status (e.g. individual, married filing jointly), and number of dependents. This information helps Betterment create a comprehensive tax profile, estimating your federal and state income tax rates, long-term capital gains (LTCG) rates, and applicable standard deductions. Betterment’s estimated tax savings methodology also incorporates the IRS' cap on ordinary income offsets for capital losses—$3,000 for most individuals or $1,500 if married filing separately, and also incorporates any available carryforward losses.
Tax lot analysis and offsetting hierarchy: At the heart of Betterment’s estimated tax savings tool is a detailed analysis of tax-lot level trading data. Betterment tallys TLH-triggered losses (short- and long-term) from other realized capital gains or losses, grouping them by year, and calculates your potential tax benefit by offsetting losses and gains by type according to IRS rules, and allowing excess losses to offset other income types or carry forward to future years. The IRS offset order is applied:
- Short-term losses offset short-term gains
- Long-term losses offset long-term gains
- Remaining short-term losses offset long-term gains
- Remaining long-term losses offset short-term gains
- Remaining short-term losses offset ordinary income
- Remaining long-term losses offset ordinary income
- Any further losses are carried forward
Current year estimated tax savings: Betterment calculates your current year estimated tax savings from TLH based on the IRS numbered offset list above, which is the sum of:
- Short-term offset represents the tax savings from subtracting your short-term harvested losses and cross-offset long-term harvested losses from current-year short-term capital gains (numbers 1 and 4 above), then multiplying by your estimated federal plus state tax rate.
- Long-term offset represents the savings from subtracting long-term harvested losses and cross-offset short-term harvested losses from current-year long-term capital gains (numbers 2 and 3 above), multiplied by your estimated long-term capital gains rate.
- Ordinary income offset captures the savings from applying any remaining harvested losses to your ordinary income up to the allowable limit (numbers 5 and 6 above), multiplied by your estimated federal plus state tax rate.
- Both short-term and long-term harvested losses may include banked losses from prior years that couldn’t be used at the time. These carryforward losses (number 7 above) are applied in the same way as current-year harvested losses when calculating your tax savings.
For the tool, Harvested Losses are all time short- and long-term harvested losses i.e., all harvested losses to date through TLH. Savings from the Short-term offset, long-term offset, and ordinary income offset are summed to yield the current year estimated tax savings.
All-time estimated tax savings : Betterment calculates your all-time estimated tax savings from TLH based on the sum of:
- All-time Long-term harvested losses × LTCG rate
- All-time Short-term harvested losses × (Federal + State tax rate)
For the all-time estimated tax figure, the all-time figures used are all your harvested losses through Betterment’s TLH feature to the present date, and rather than calculate offsets, Betterment assumes that you are able to fully offset your long-term harvested losses and short-term harvested losses with gains. Therefore, we apply the long term capital gains rates and marginal ordinary income rate (which is the sum of your federal and state tax rates) by your total long-term harvested losses and short-term losses, respectively. There is no ordinary income offset in the All-Time Estimate. This simplification does not track when the loss occurred, and therefore, assumes current estimated tax rates were applicable throughout prior years.
Assumptions: While this tool provides a powerful estimate of your potential tax benefits from tax loss harvesting, it is important to understand the assumptions and limitations underlying the estimated tax savings calculations. Estimated tax savings figures presented are estimates—not guarantees—and rely on the information you’ve provided to Betterment. Actual tax outcomes may vary based on your actual tax return and situation when filing. The tool evaluates only the activity within your Betterment accounts and does not take into account any investment activity from external accounts. For the current year calculation, the tool also assumes that you have sufficient ordinary income to fully benefit from capital loss offsets, and for the all-time calculation, the tool provides a tax-dollar estimate of all harvested losses, based on type (short- or long-term) and current tax rates.
Additionally, the estimated tax savings calculation simplifies the treatment of certain entities; for example, trusts, business accounts, or other specialized tax structures are not handled distinctly. State-level tax estimates exclude city tax rates and municipal taxes, which may also affect your overall tax situation. The “all-time estimate” shown reflects an approximation of the total tax impact of harvested losses to date—including benefits that have not yet been realized or claimed.
While the estimate has its limitations, it provides a clear and actionable view into how tax-smart investing can add value over time. It helps show how harvested losses may lower your tax bill and boost after-tax returns—bringing transparency to a strategy that’s often hard to see in dollar terms. For many investors, it highlights the long-term financial benefits of managing taxes proactively.
Conclusion
Summary: Tax loss harvesting can be an effective way to improve your investor returns without taking additional downside risk.
